Building Tree Driven ACL & Nested Permissions for Secure FinTech Applications - Sprintmoney

In this technical deep-dive, we'll explore how we implemented a sophisticated permission system that enables rapid onboarding of 50,000+ bank employees for Employee Masters across major banks. Our solution leverages tree data structures for efficient access control and permission management.
Problem Statement
Sprintmoney approached us to develop a SaaS solution for banks that would:
-
Handle sales of Insurance, Mutual Funds, and Loan Against Securities (LAS)
-
Function as a white-label solution deployable in banks' own cloud infrastructure
-
Support direct employee onboarding with proper permissions
Banks typically follow a hierarchical organizational structure which are generally based on Basel Committee Corporate Governance Principles for Banks or Open Banking Specification.
Here is a simplified version
Bank-level Organization
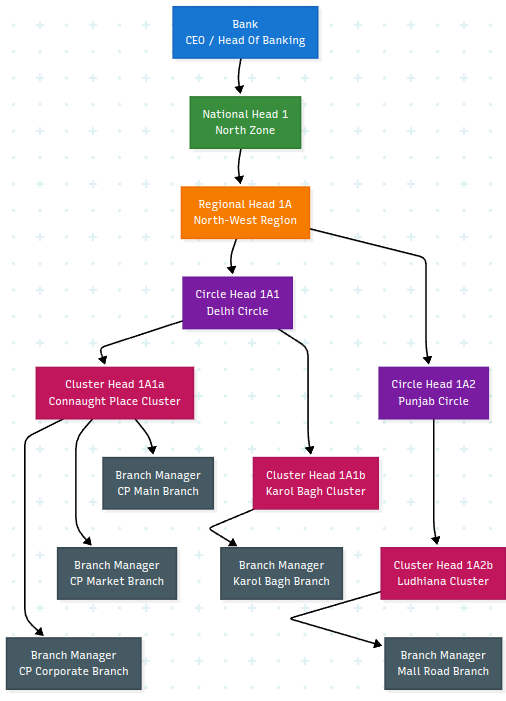
Similarly, Each Branch then has its own hierarchy
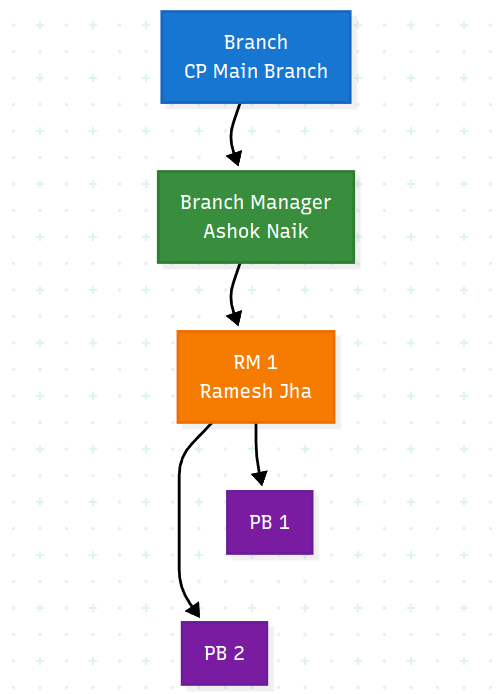
Sprintmoney expected a solution that could be flexible enough, such that
-
Seamlessly integrate with any major bank's employee master data
-
Implement document/entity-specific permissions (Leads, Targets, Rewards) based on organizational hierarchy
-
Enable granular permission management by respective managers
-
Support reward point propagation through the organizational structure
User Story
Actor: Lead Generator
A root-level employee who interacts with customers and creates leads for potential requirements.
[Lead Generator] => [Customer Details] => [Lead Created]
Actor: Specified Person
A certified person who has the legal authority to sell a product and close the lead
[Existing Lead] => [Follow Up] => [Sales Funnel]
=> [Sales Complete] => [Rewards Allocated]
=> [Closed]
Actor: Branch Manager
A manager who tracks branch-level performance and accounts, targets, and rewards
[Rewards Allocated] => [Targets Updated]
Expected Reward Propogation
If 2 Lead Generator Create 2 leads of INR 30,000 and 42,000 each, and they endup being sold, this is the expected flow of rewards (Eg. Targets).
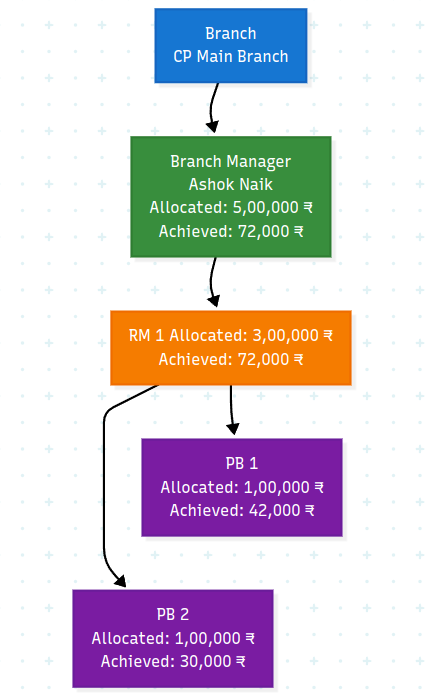
The same propagation of rewards is expected throughout both trees.
Solution
Tree Data Structure Implementation
With a segregated tree for each Bank & Branch organization, we can have a structure that would simplify
-
Read Performance
-
Efficient data retrieval
-
Hierarchical caching
-
Quick permission checks
-
-
Update Management
-
Asynchronous event processing
-
Branch-level sharding
-
State management
-
The solution links the lowest non-group node from the Bank Tree to the root node of the Branch Tree , creating a seamless hierarchy while maintaining separation of concerns.
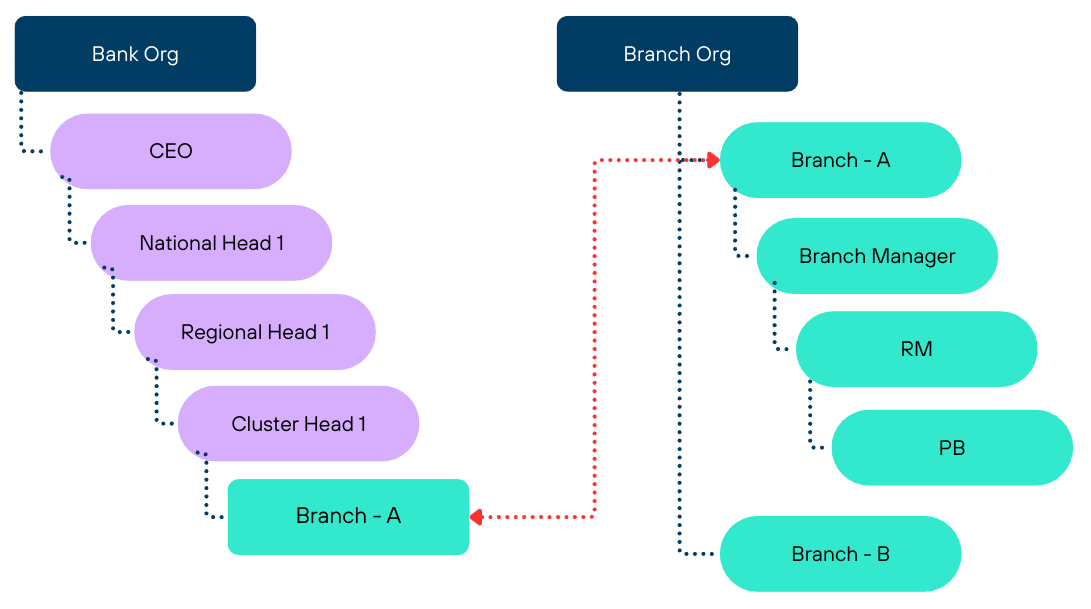
This architecture provides independent processing trees that can bifurcate handling of different entities and document types (Leads, Targets, Rewards, etc.), with transactional synchronization at the Branch level and asynchronous background synchronization at the Bank level.
Bulk Import Architecture
For importing a bulk of masters and appending the respective ACL is a write-heavy operation, with simple jobs or direct enqueue, it becomes tricky as missing out organization nodes or them not being in the correct sequence could cause errors and a fallback loop.
S3-Based Batch Processing
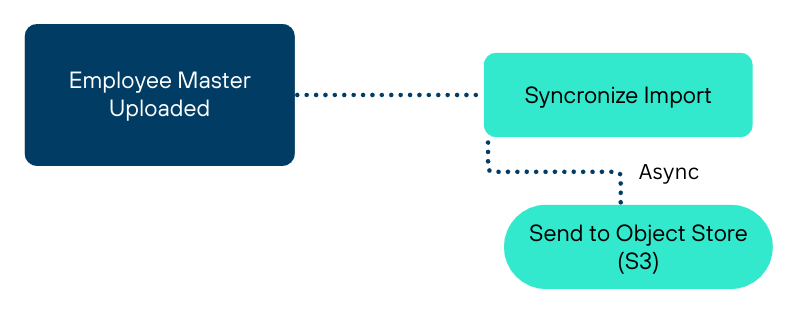
Hierarchical Pre-population
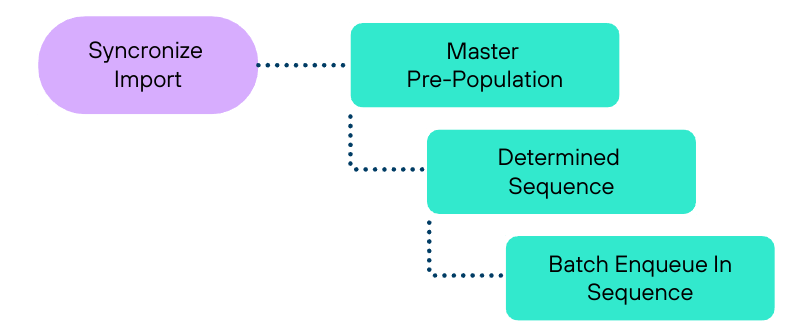
For having master's imported, we made jobs that would batch process masters and first specify the hierarchy in which the masters should be synced in.
Performance Optimization
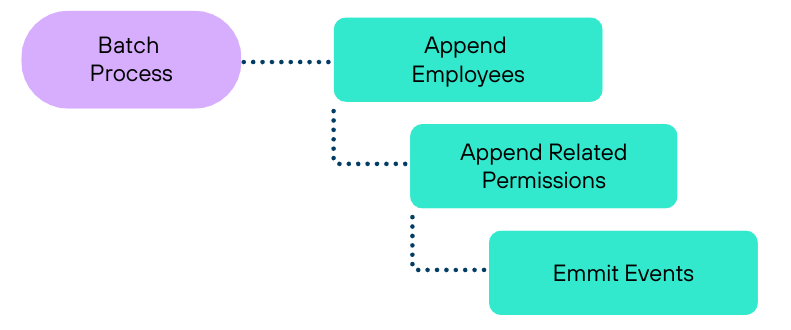
With the organization tree pre-populated, we were able to append masters in seconds.
Sharding & Caching Strategy
Our solution implements:
-
-
Bank + Branch identifiers
-
User-specific access patterns
-
-
-
Branch-level data isolation
-
Reduced database load
-
Improved query performance
-
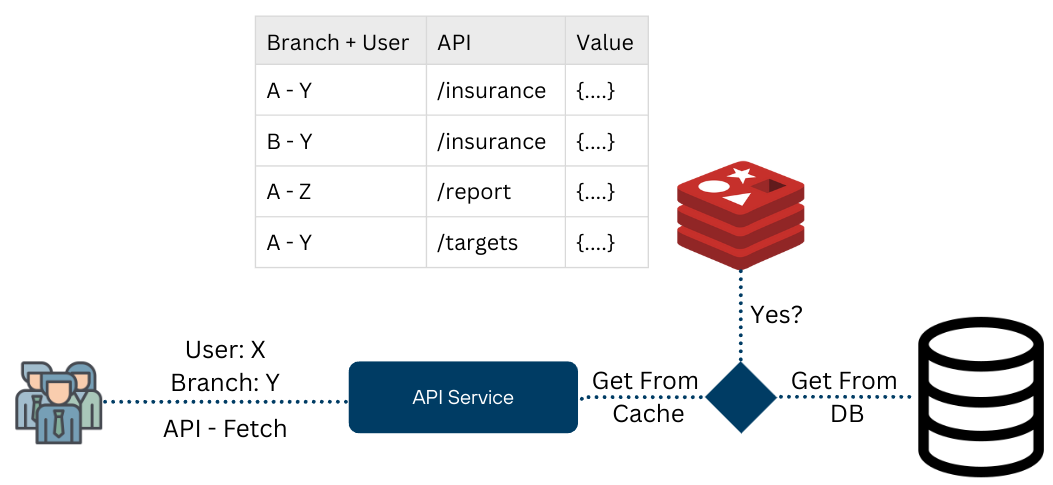
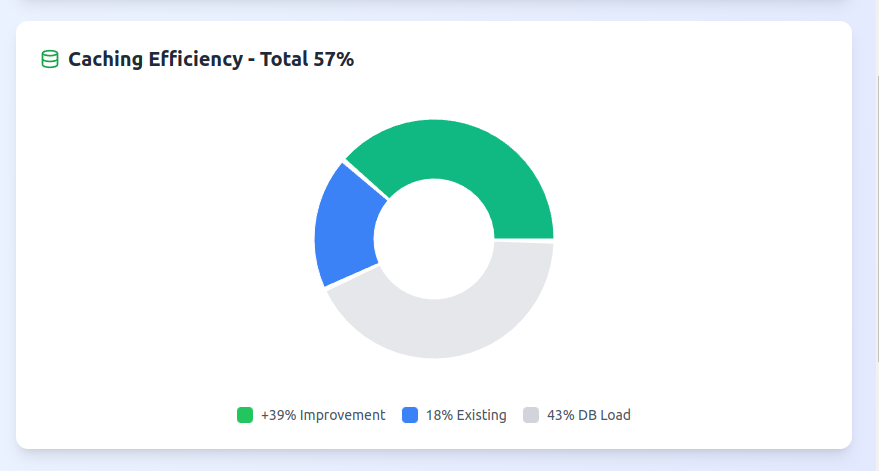
With achieved virtual sharding, we would yield great performance in terms of latency and highly improve caching, significantly reducing any load on the DB.
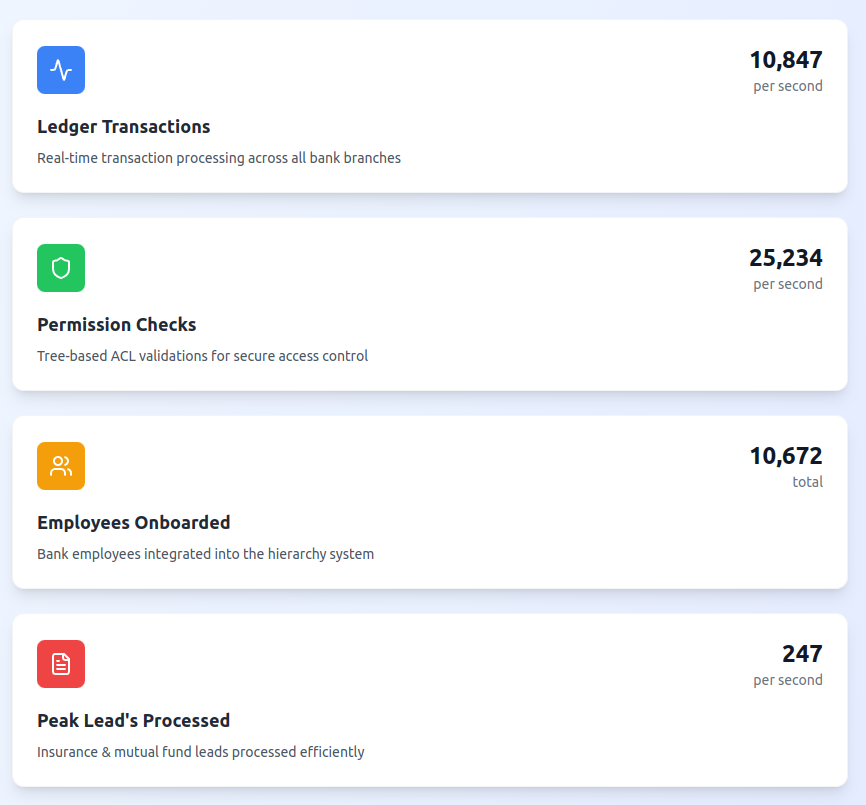
Business Impact & Performance
Caching Improvements
Conclusion
This architecture demonstrates how thoughtful system design can turn scaling challenges into opportunities for performance optimization. The tree-based approach not only solved the immediate permission management needs but also provided a foundation for horizontal scalability.
Author: Prafful Suthar
Ready to solve a similar problem? Scalix.in
© Copyright 2026. All Rights Reserved.